
When using APA format, follow the “author-date” method of in-text citation. APA Citation Rules: The Basics Order and structure of in-text citation content
#How to properly cite sources apa generator#
Before submitting your manuscript to a journal or publisher, be sure to use our free APA citation generator for your references and in-text citations. This resource provides detailed guidelines for citing sources in your paper and includes examples of in-text citations for reference by research authors.
#How to properly cite sources apa manual#
For more information, consult the APA Style Manual website. The following guidelines and examples are taken from the APA Publication Manual, 6th edition, 2nd printing, which details rules and application of APA style in research papers, including in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and references. In research papers, in-text citations are most commonly used in the Introduction and Discussion Results sections. We are not going into such differences here but will focus on the correct way of referencing other people’s research in your own paper according to one of the most common styles used to cite sources within the social sciences and in several other academic disciplines, that is, APA (American Psychological Association) style.
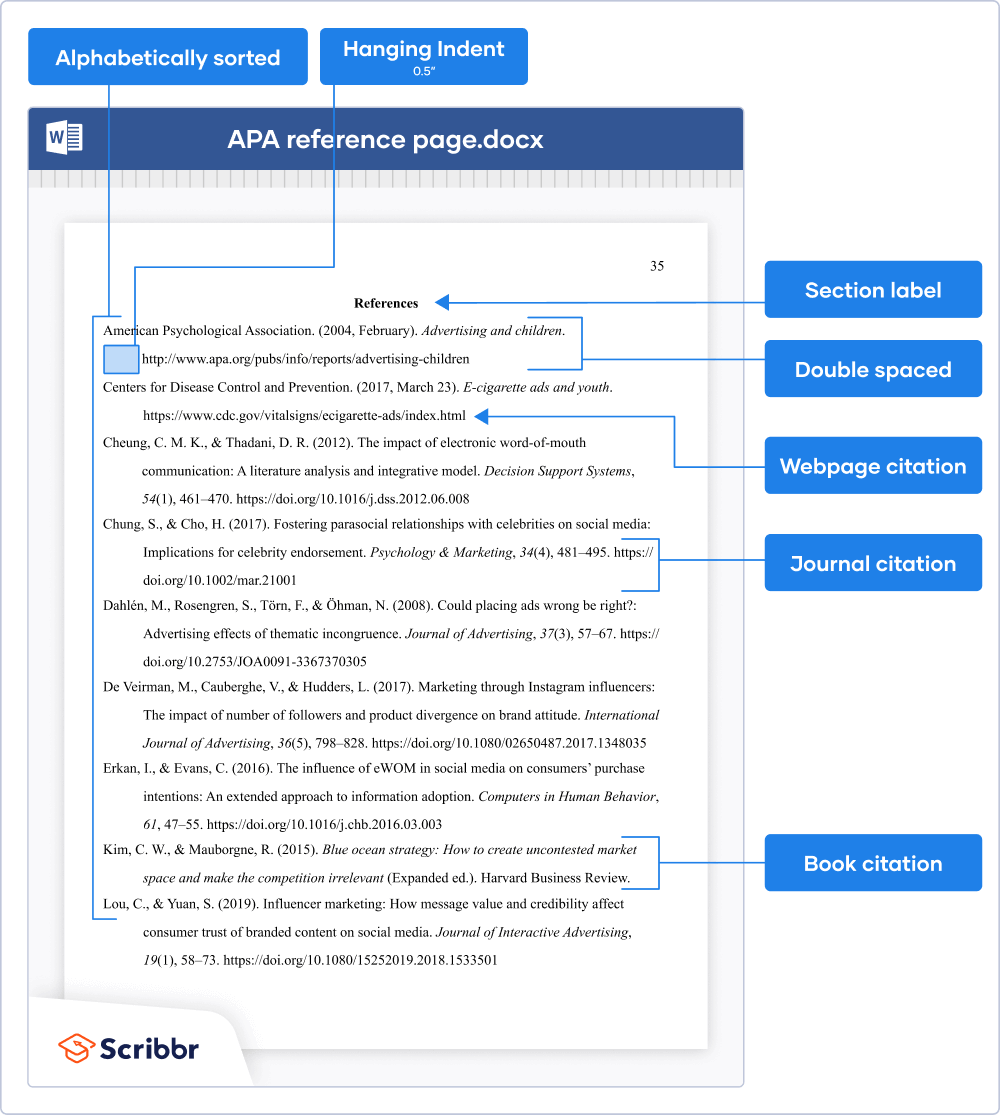
General rules for what information should be provided when citing sources in a research paper vary across fields and depend on the type of source (e.g., books, journal articles, patents, conference proceedings, websites, etc.). This is not only an ethical question, as being “sloppy” with your sources can easily be considered plagiarism (and even self-plagiarism, if you fail to refer to your own work), which can have legal consequences and damage your reputation. The rationale behind citing other people’s publications in your own manuscript is that you want to avoid intellectual dishonesty by giving credit to whoever reported a finding first or invented a specific technique. In addition, every time a work is cited within a paper (in APA style, a parenthetical citation), a corresponding entry must be included in the reference list. (The College of St.When writing a journal article, literature review, convention paper, or any other academic document, authors must include in-text citations whenever they refer to, summarize, paraphrase, or quote from another source. Group Authors with Identifiable Abbreviations: This is agreed upon (Smith & Long, 2019).Ĭiting more than one work by same author published in the same year Source has more than one author in reference This has evidence ( Quote from website – use paragraph numberĪccording to, “…” (Smith, 2019, para. Italics for books & journals, “quotation marks” for articles & web pages

No author – give title of work abbreviated to first major word At the end of the quote put the period after the last word of the sentence followed by the parentheses. If your quote is forty words or more, set it off in a block text by beginning a new line, indenting one inch, and do not add quotation marks. The punctuation for the sentence goes AFTER the parenthesis. Make sure the source information in parentheses matches with your works cited. Only use page numbers for a direct quote. Give the author’s last name and the publication year. There are slight differences depending on which style you are using.

Put the information about the source in parentheses in the text of your paper as opposed to a footnote where the source information is at the bottom of the page or an endnote where it goes at the end of your paper. In order to avoid plagiarism, it is extremely important that you cite all words and ideas that you got from somewhere else.

This is more obvious when you are directly quoting from a source, but it is also needed when you have summarized or paraphrased from a source and even if you got an idea from somewhere else. Parenthetical documentation or in-text citations tells the reader where you got any and all information that did not come from inside your own head.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
